Theme:
Clinical Microbiology-2020
Conference Series LLC LTD, the world’s leading Scientific Event Organizer invites all the Speakers, Delegates, Researchers, Students and Industrialists to attend 11th World Congress on Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (Clinical Microbiology 2021) during March 15-16, 2021 Webinar. Around the theme Novel Insights and Innovations in Clinical Microbiology. Following the success of previous Microbiology Conferences held during November 16-17, 2020 Webinar . We are now delighted to welcome you to 11th World Congress on Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (Clinical Microbiology 2021) during March 15-16, 2021 Webinar. Aimed to provide an opportunity for all the Attendees to meet, interact and exchange new ideas in the various areas of Microbiology.
This intriguing event has taken the initiative to gather the world class experts both from Academic and Industry in a common platform at Clinical Microbiology 2021 Conferences to share their recent research finding to the world and enlighten other esteemed delegates on latest trends in the field of Clinical Microbiology. We cordially invite all concerned people from different countries of Europe (UK, London, Spain, Istanbul, Denmark, Netherlands, Germany, France, Italy, Brazil, Turkey) and Asia countries Israel, India, China, Japan to come join us at our event and make it successful by your participation.
Dear Colleagues and Friends,
Welcome and warmest wishes!
It is a great honor to have the opportunity to invite all the Speakers, Delegates, Researchers, Students and Industrialists to attend 11th World Congress on Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (Clinical Microbiology 2021) during March 15-16, 2021, Webinar. Our commitment to discuss the new technology, the new products, the service your industry may bid to a broad international audience and scientific innovations with one another will truly embody this year’s theme, “Novel Advancements and Therapeutic Acuities in Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases”.
By sharing new technology participating in forums and collaborating with one another, your work will continue to impact many lives and truly benefit the scientific community. I wholeheartedly welcome you to share your knowledge, experience and creative idea in this conference through interacting with worldwide experts from the recent researches on Microbiology Applications. The conference includes Keynote lectures, Oral and Poster presentations. On behalf of the Organizing Committee Clinical Microbiology 2021 of we would like to express our warmest welcome to all of you who are participating in Clinical Microbiology Summit 2021, and hope you will enjoy .
Why to attend?
Clinical Microbiology 2021 is a unique and exciting opportunity, have been designed in an interdisciplinary manner with a multitude of tracks to showcase the new technology, the new products, and the service your industry may bid to a broad international audience. It covers a lot of topics and it will be a nice platform to showcase their recent researches on Clinical Microbiology Applications. Clinical Microbiology 2021, host presentations from experts across the world in the field of microbiology and anticipates more than 200 participants around the globe with thought provoking Keynote lectures, Oral and Poster presentations. The attending delegates comprise Editorial Board Members of associated global journals.
Business networking is an avenue for vendors to have network and B2B meetings with “Top Scientists and Colleagues” and with an effective low-cost marketing method for developing sales and opportunities and contacts. Student Poster Competition is organized at event, to inspire students and recent alumnae to present their unique research which will be later published in the journals. All accepted abstracts will be presented at the poster sessions during the conference. An opportunity to present E-Poster for all the students who cannot attend the conference at 199$ with abstract published in the website with DOI number Live Streaming is a value-added service offering to Speaker.
Young Scientist Benefits
- Our conferences provide best Platform for your research through oral presentations.
- Share the ideas with both eminent researchers and mentors.
- Young Scientist Award reorganization certificate and memento to the winners
- Young Scientists will get appropriate and timely information by this Forum.
- Platform for collaboration among young researchers for better development
- Award should motivate participants to strive to realize their full potential which could in turn be beneficial to the field as whole.
Deadline for Registrations:
Platform for collaboration among young researchers for better development
- Till November 30, 2021– $399
- Till December 31, 2021 – $499
- Till January 10, 2021 – $599
We look forward to seeing you in our Webinar.
Track 1 : Clinical Microbiology:
Clinical Microbiology is a branch of medical science which mainly deals with the prevention, diagnosis, epidemiology and treatment of infectious diseases. It is concerned about different clinical applications of microbes for the improvement of health. Clinical Microbiology plays a key role in patient care by providing the cause of infection and antimicrobial susceptibility data to physicians. Rapid diagnosis of pathogens is mandatory for the successful administration of antibiotics and to increase treatment rates. It has various methods of analysis used to identify and isolate the microbes.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM)
Track 2: Types of Vaccines:
A vaccine is a substance that is introduced into the body to stimulate the immune response. It is given to prevent an infectious disease for developing the person becoming ill. It is made up of using several different processes. It made from microbes that are dead so they are unable to cause disease. Merely segments of the pathogen (this includes both sub unit and conjugate vaccines). If the vaccinated person then comes into contact with the disease-causing microbe, the immune system remembers the antibodies it made to the vaccine and can make them earlier .The person is claimed to be resistant to the pathogen.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 3: Infectious diseases & its types:
Infectious diseases can be caused by many pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites which will cause illness and disease. For humans, transmission of pathogens may occur in a variety of ways. Spread from person-to-person by direct contact, water or food-borne illness of infected particles in the environment and through insects (mosquitoes) and ticks. Mild infections to take rest and home remedies, while some life-threatening infections may have hospitalization.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM)
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM)
Track 4: Food Microbiology:
Food Microbiology is the flora and sources of microorganisms in food. Methods of detection and enumeration of microorganisms in foods. Intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of food that effects of microbial growth and survival. Roles of microorganisms in spoilage, food borne diseases and in food products. It preservatives the quality control and microbiological standards. It is the source of food to man are of the plant and animal origin. Food safety may be a major focus of food microbiology.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 5 : Clinical Bacteriology & Virology:
Clinical bacteriology is the study of bacteria and their relation to medicine and to other areas such as agriculture and industry. These are the single-celled microorganisms which can live as independent organisms or dependently like a parasite. Clinical microbiologists use microscope to look at smears of original samples to get early information.
Clinical virology is that the study of viruses and virus-like agents, including their classification, disease-producing properties and genetics. It is often considered a neighborhood of microbiology or pathology. Viruses have conventionally been viewed in a negative milieu responsible for diseases; however viruses also have certain beneficial properties that can be exploited for useful purposes such as role of virus in gene therapy.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
Track 6: Microbial Biofilms:
Biofilms are the aggregation of microbial cells, which are associated with the plaque, pond scum, or the slimy build up in sink. This formation involves sequence of steps like conditioning, attachment, metabolism, and detachment. It consists of water channels, EPS (Exopolysaccharide), and EDNA (Environmental DNA), which plays an important role in nutrient circulation, its development, and structure stabilization. Resistance of planktonic bacteria against antimicrobial agents gets increased on the formation of biofilm, which may be the presence of diffusive barrier EPS or neutralizing enzyme, cells undergoing starvation, or due to spore formation. There are numerous factors, which affects biofilm formation such as substratum effects, conditioning film on substratum, hydrodynamics, characteristics of the aqueous medium, cell characteristics, and environmental factors. It can cause industrial, medical, and household damage and is a reason for loss of billions of dollars every year. Development of biofilm on catheters, medical implants. A major cause of infections and surface in almost an irreversible manner. It exists in variety of forms like dental diseases in humans. Examples include Plaque, Native Valve Endocarditis, Otitis media, Prostatitis, Cystic fibrosis, Periodontitis, Osteomyelitis, etc.,
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 7 : Clinical Veterinary Microbiology:
Veterinary microbiologists learn to recognize external signs of infection or animal behaviors that point to an infection. It also learns the internal and population-wide progression patterns of infectious agents, as well as measures of control and prevention. It is the branch of study mainly focused on microbes that are causing diseases to animals. Veterinary pathology helps in the diagnosis of diseases caused to animals such as dogs, cows, etc. veterinary medicine is widely practiced by pathologist for the well-being of animals.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 8 : Cellular microbiology:
The term “cellular microbiology” was identifying an emerging discipline integrating the fields of cell biology and microbiology. The advent of genomics, proteomics, and post genomics has resulted in widespread understanding of the field of cellular microbiology among scientists. It is the scientific study of the properties of microbial cells. It combines techniques and approaches of classic cell biology and microbiology.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 9 : Pharmaceutical Microbiology:
Pharmaceutical Microbiology is an applied branch of Microbiology. It involves the study of microorganisms related to the manufacture of pharmaceuticals. It minimizing the number of microorganisms in a process environment, and ensuring the finished pharmaceutical product is sterile. Other aspects of pharmaceutical microbiology include the research and development of anti-ineffective agents. With both sterile and non-sterile products, the consequences can range from discoloration to the potential for fatality. The Pharmaceutical Microbiology evolved for pharmaceutical microbiology testing, including antimicrobial effectiveness testing.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 10: Antimicrobial agents:
Antimicrobial agent is a large variety of chemical compounds and physical agents that are used to destroy microrganisms to prevent their development. These medicines are often grouped consistent with the microorganisms they act primarily against. The antibiotics are used against bacteria, and anti fungal are used against fungi. . Agents that kill microbes are microbiological, while those that merely inhibit their growth are called bio static. While the utilization of antimicrobial medicines to stop infection is understood as antimicrobial prophylaxis.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 11: Immunization Infections:
Immunization is that the process whereby an individual is formed immune to a communicable disease typically by the administration of a vaccine. Vaccines stimulate the body’s own system to guard the person against subsequent infection or disease. It may occur naturally when people are exposed to bacteria or viruses or doctors may provide it through vaccination. Types of Immunization:
There are two types of immunization:
- Active immunization
- Passive immunization
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 12 : Emerging Diseases
Emerging infectious diseases are infections that have recently appeared within a population or those whose incidence or geographic range. These infections account for at least 12% of all human pathogens which will have evolved from a known infection (e.g. influenza) or spread to a new population (e.g. West Nile fever) or to a neighborhood undergoing ecologic transformation (e.g. Lyme disease), They also include infectious diseases that have affected a given area in the past, declined with passage of time or were controlled, but again reappeared in increasing numbers. Sometimes, an old disease reappears during a new clinical form which will often be severe or fatal.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 13: Parasitic & Bacterial Diseases:
A parasitic disease, also referred to as parasitosis, is an infectious disease caused by a parasite. Many parasites do not cause diseases as it may eventually to death of both organism and host. Parasites infecting human beings are called human parasites. The parasite infections of animals (production and pets) affect the health and quality of animal life, the parasites frequently present a microbial associated which play several functions, like nutrition, reproduction or defense against the host system.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 14 : Mycobacterial infections:
Mycobacterium may be a genus of Actinobacteria, given its circle of relatives, the Mycobacteriaceae. Over 190 species are recognized in this genus. The most notable mycobacterial infections are those that are caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and Mycobacterium lepra it is a type of germ. There are many different kinds. The most common one causes tuberculosis. Another one causes leprosy. . They aren't "typical" because they don't cause tuberculosis. But they will still harm people, especially people with other problems that affect their immunity, like AIDS.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 15: Antimicrobials/Antibiotics/Antibacterial Resistance:
It is ability of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi or protozoans to grow despite exposure to antimicrobial substances designed to inhibit their growth. Microbes can evolve antimicrobial resistance. The term antibiotic resistance may be a subset of, because it applies only to bacteria becoming immune to antibiotics. Resistant microbes are more difficult to treat, requiring alternative medications or higher doses of antimicrobial and sometimes impossible, to treat. Antibiotic resistance doesn't mean the body is becoming immune to antibiotics; it is that bacteria became immune to the antibiotics designed to kill them.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM)
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
Track 16: Infection Control, Disease Diagnosis and Prevention:
Every year, lives are lost due to the spread of infections in hospitals. Health care workers can take steps to stop the spread of infectious diseases. These steps are part of infection control. Proper hand washing is that the best thanks to prevent the spread of infections in hospitals. If you're a patient, do not be afraid to remind friends, family and health care providers to scrub their hands before getting on the brink of you. It is grounded in infectious diseases, epidemiology, science and health system strengthening. It occupies a singular position within the sector of patient safety and quality universal health coverage since it's relevant to doctors and patients at every single health-care encounter.
EUROPE: International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Antiviral Research (ISAR), Interregional Russian Microbiological Society, The Interregional Association for Clinical International Society for Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (IACMAC), Russian Medical Society, Federation of European Microbiological Societies (FEMS), International Society of Chemotherapy Infection and Cancer (ISC), Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM), British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC), Society for Applied Microbiology (SfAM).
USA: American Society for Microbiology (ASM), Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (SIMB), Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), American Association of Immunologists (AAI), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research (SABER).
ASIA-PACIFIC: Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies (FAPMS), International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), Chinese Society for Microbiology (CSM), Japan Applied Microbiology Society, Philippine Society for Microbiology (PSM).
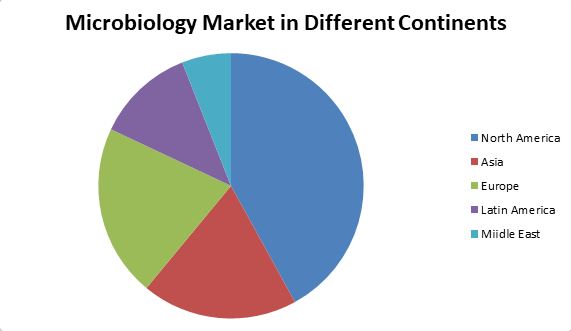
The Microbiology Testing/Clinical Microbiology market worldwide is projected to grow by US$1.8 Billion, driven by a compounded growth of 6.1%. Instruments, one of the segments analyzed and sized in this study, displays the potential to grow at over 5.8%. The shifting dynamics supporting this growth makes it critical for businesses in this space to keep abreast of the changing pulse of the market. Poised to reach over US$1.6 Billion by the year 2025, Instruments will bring in healthy gains adding significant momentum to global growth.
Representing the developed world, the United States will maintain a 5.3% growth momentum. Within Europe, which continues to remain an important element in the world economy, Germany will add over US$64.3 Million to the region's size and clout in the next 5 to 6 years. Over US$56.2 Million worth of projected demand in the region will come from the rest of the European markets. In Japan, Instruments will reach a market size of US$70.8 Million by the close of the analysis period. As the world's second largest economy and the new game changer in global markets, China exhibits the potential to grow at 9% over the next couple of years and add approximately US$487.9 Million in terms of addressable opportunity for the picking by aspiring businesses and their astute leaders.
Presented in visually rich graphics are these and many more need-to-know quantitative data important in ensuring quality of strategy decisions, be it entry into new markets or allocation of resources within a portfolio. Several macroeconomic factors and internal market forces will shape growth and development of demand patterns in emerging countries in Asia-Pacific, Latin America and the Middle East. All research viewpoints presented are based on validated engagements from influencers in the market, whose opinions supersede all other research methodologies.
Competitors identified in this market include:
3M Company
Abbott Laboratories
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Becton, Dickinson and Company
bioMerieux SA
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Bruker Corporation
Danaher Corporation
Hologic, Inc.
Merck KgaA
Neogen Corporation
Qiagen NV
Roche Diagnostics (Schweiz) AG
Shimadzu Corporation
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
Region Segmentation of Microbiology Testing/Clinical Microbiology Market:
North America Country (United States, Canada)
South America
Asia Country (China, Japan, India, Korea)
Europe Country (Germany, UK, France, Italy)
Other Country (Middle East, Africa, GCC)
Conference Highlights
- Clinical Microbiology
- Types of Vaccines
- Infectious diseases & its types
- Food Microbiology
- Clinical Bacteriology & Virology
- Microbial Biofilms
- Clinical Veterinary Microbiology
- Cellular microbiology
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology
- Antimicrobial agents
- Immunization Infections
- Emerging Diseases
- Parasitic & Bacterial Diseases
- Mycobacterial infections
- Antimicrobials/Antibiotics/Antibacterial Resistance
- Infection Control, Disease Diagnosis and Prevention
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 16-17, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by